What Is the Orientation of Images Formed on the Retina
From the center of the optic nerve radiates the major blood vessels of the retina. The rods and conses are distributed in the retina in large numbers.
What Is The Type Of The Image That Is Formed On The Retina When We See An Object Quora
And its a real image.
. To the right of the eye and the image is formed at the intersection of real. For a familiar. Up to 24 cash back Light falls on retina on inner side ie.
The center of the image falls on the fovea which has the greatest density of light receptors and. When an image goes through the eyes the image that forms in the retina is upside down and the brain has to flip it back the right way. Finally we note that a virtual image is upright and larger than the object meaning that the magnification is positive and greater than 1.
For people who are nearsighted images come into focus in. Upside down and reversed to left to right. An image is formed on the retina with light rays converging most at the cornea and upon entering and exiting the lens.
As the image is inverted by. We can see the magnified image with our eyes because the lens of the eye converges the rays into a real image projected on our retina. The flexible lens of the eye allows it to adjust the radius of curvature of the lens to produce an image on the retina for objects at different distances.
Because the optics are shift-invariant and there is no frequency-dependent phase shift the retinal image of a cosinusoid at frequency is a cosinusoid scaled by a factor. Both conditions are easily corrected with optical lenses. Orientation of the image.
Some scientists believe that when were first born we see the world upside down. The retinal image size of a familiar object is a strong monocular depth cue. The magnification of a converging lens is by definition M -Y2Y1 -X2X1.
It is a minute area of 1 mm in center of retina. Its composed of several layers including one that contains specialized cells called photoreceptors. The visual field is that area in space perceived when the eyes are in a fixed static position looking straight ahead.
What part of the eye is affected by cataracts. - upside down and reversed left to right - right and left are reversed only - enlarged and upside down only - upside down only. The Formation of Images on the Retina Because light rays diverge in all directions from their source the set of rays from each point in space that reach the pupil must be focused.
The formation of focused images on the photoreceptors of the retina depends on the refraction bending of light by the cornea and the lens Figure 112. The light image falling on the retina is sensed by two types of biological light sensors. Rays from the top and bottom of the object are traced and produce an inverted real image on the retina.
It is the muscular adjustment of the lens known as accommodation that focuses the image directly on the retina. Central portion of macula called fovea centralis. The retinal image passes back through the optics and is scaled again so that the measurement would be a cosinusoid scaled by the factor.
One is called rod and the other is called cone. There are two types of photoreceptor cells in the human eye rods and cones. If this adjustment is not correctly accomplished the viewer suffers from either nearsightedness or farsightedness.
The distance to the object is drawn smaller than scale. The retina is the sensory membrane that lines the inner surface of the back of the eyeball. This is composed entirely of cones.
It provides acute and detailed vision. An image is formed on the retina with light rays converging most at the cornea and upon entering and exiting the lens. What is the orientation of images formed on the retina.
Rod photoreceptors detect motion provide black-and. The light rays get smaller allowing the entire image to fit through the pupil and form a complete image on the retina albeit upside down and reversed. This is because light travels in a straight path and so the image of the outside world formed on the retina is inverted.
When an ophthalmologist uses an ophthalmoscope to look into your eye he sees the following view of the retina Fig. Rays from the top and bottom of the object are traced and produce an inverted real image on the retina. Spatial Orientation and the Visual Field.
Without this reversal we would have a very limited view of our world. Hence had Campbell and Gubisch used a cosinusoidal input stimulus we. The retina on which the image is focused by the eye lens is inverted form.
For people who are farsighted images come into focus behind the retina. In the center of the retina is the optic nerve a circular to oval white area measuring about 2 x 15 mm across. Its the brain that eventually learns to re-invert the image.
Pigmented layer of retina contains black pigment ie. The retina itself is a complex tiling of photoreceptors. The closer object projects onto a larger number of photoreceptors which cover a larger portion of the retina.
The brain automatically reorients this. The fibrous covering of the eye consists of the white outer layer known as the _____ and a transparent position known as the _____. The image that appears on the retina is upside down and small.
The image formed by eyes lens system is smaller than the object viewed inverted upside-down Figure 146 and reversed right-left Figure 147. Recall the 3D appearance of Figure 123 c. What is the orientation of images formed on the retina.
On inner limiting membrane. When light passes through the lens it is inverted so light that hits the top of the retina comes from the bottom of the field of view and the light on the left of the retina comes from the right part of the field of view. Many cues result from the geometric distortions caused by perspective projection.
Nerves on the retina stimulate an impulse to the brain via the optic nerve where the image is seen as right side up.

Diabetic Retinopathy Eye Growth Of Abn Bvs And Hemorrhage Leads To Retinal Scarring And Finally Retinal Deta Diabetic Retinopathy Diabetes Causes Of Diabetes
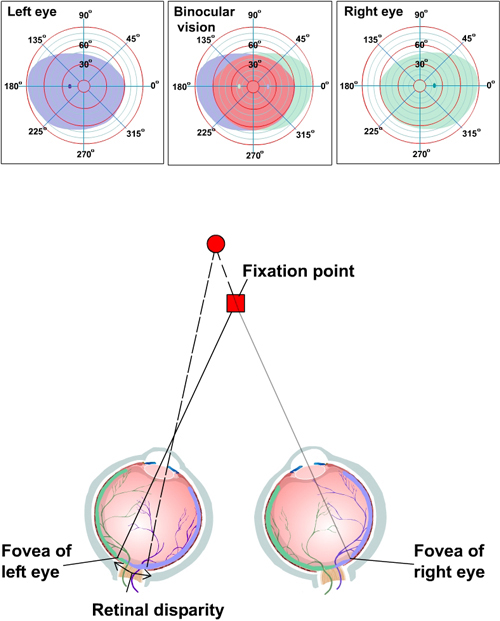
Visual Processing Eye And Retina Section 2 Chapter 14 Neuroscience Online An Electronic Textbook For The Neurosciences Department Of Neurobiology And Anatomy The University Of Texas Medical School At Houston

A P Test 4 Image 6 Flashcards Quizlet

Focal Length Of A Lens Physics And Mathematics Physics Classroom Physics
No comments for "What Is the Orientation of Images Formed on the Retina"
Post a Comment