Describe the Three Different Forms of Schwann Cells
There are three types of glial cells in the mature central nervous system. Describe the three types of neurons classified on the basis of structure.

What Is The Role Of Neuron Schwann Cells Quora
What Are Glial Cells and What Do They Do.

. Their main purpose is to help information move. Schwann cells such as oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system form a myelin sheath around the axons of the nerve cells or neurons 3. Gaps in the myelin sheath of the axons of peripheral neruons.
Form the blood brain barrier Surround the soma and insulate it Produces the CSF 5. Produces myelin around a singular b. Radial glial cells are progenitor cells that can generate neurons astrocytes and oligodendrocytes.
Since the spinal cord is part of the central nervous system oligodendrocytes form this myelin. Schwann cells myelinate the nerve cells that project to and from our muscles internal organs and the other signals in the peripheral nervous system. Astrocytes oligodendrocytes and microglial cells Figure 14ACAstrocytes which are restricted to the brain and spinal cord have elaborate local processes that give these cells a starlike appearance hence the prefix astro.
Pair the neuroglia with their function. Supporting cells of the peripheral nervous system responsible for the formation of myelin. Astrocytes oligodendrocytes microglia and ependymal cells located in the Central Nervous System.
Cell body and Schwann cells survive and stay active. The first three types of cells are found in the central nervous system and Schwann cells are found in the peripheral nervous system. This type of conduction is called saltatory conduction.
Glial cells of the b peripheral nervous system include Schwann cells which form the myelin sheath and satellite cells which provide nutrients and structural support to. 2 bipolar neuron two processes 1 axon and 1 dendrite specialized parts eyes nose ears 3. Ependymal cells produce cerebrospinal fluid that cushions the neurons.
Axon myelin sheaths distal to the damage. For one oligodendrocytes are only found in the central nervous system - the brain and spinal cord. Peripheral Nervous System Schwann cells.
Myelinate CNS axons and provide structural framework -Astrocytes. Schwann cells which form myelin sheaths around 1. 1 multipolar neuron one axon rest of dendrites.
Anatomy and Physiology questions and answers. The receives the signal the _ conducts the nerve impulse and the --______ contains the. The major function of astrocytes is to maintain in a variety of ways.
Glial cells also known as neuroglia are an essential part of the nerve tissue. The supporting cells of the peripheral nervous system are Schwann cells and amphitic satellite or capsular cells that are present in ganglia. Describe the different types of supporting cells known as neuroglia in the CNS.
Action potentials can hump from node to node thus increasing the speed of conduction saltatory conduction. These cells are found in different parts of the nervous system. Mostly in brain and spinal cord.
There are different types of glial cells in the nervous system such as astrocytes Ependymal cells oligodendrocytes microglia and Schwann cells. Also there are different types of glia and this is determined by their location and function. Complete the following paragraph to describe different nervous tissue types.
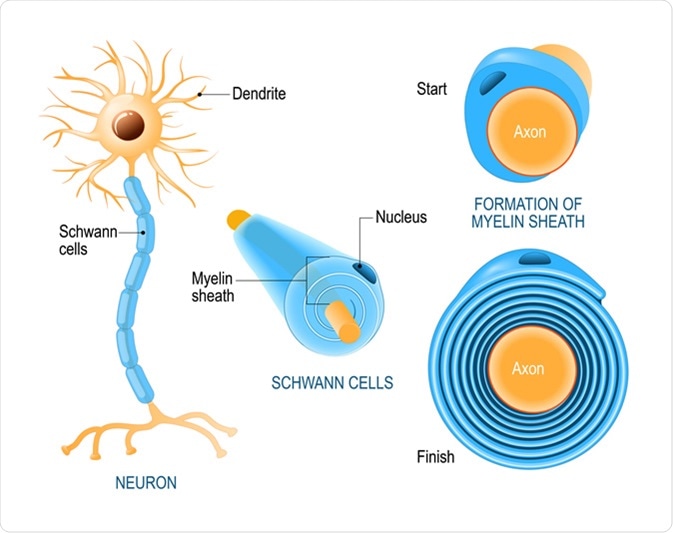
Schwann cells are named after Theodor Schwann who was a German physiologist who discovered these types of cells in the 19th century. Between adjacent Schwann cells is a small gap called a node of Ranvier where the nerve fiber is exposed. Similar to oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system Schwann cells myelinate neurons in the peripheral nervous system.
Oligodendrocytes- form myelin sheths around CNS axons. Wraps many fibers with myelin e. Schwann cell also called neurilemma cell are a type of large neurological cell responsible for forming the myelin sheath around the neurons of the peripheral nervous system and supplying nutrients to.
Functionally oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells perform the same role but structurally they are different. Maintain blood brain barrier structural support regulate ionnutrientgas concentrations absorb and recycle neurotransmitters form scar tissue after injury. Oligodendrocytes come from neural stem cells.
When a nerve impulse is conducted along a myelinated fiber it jumps from node to node. The most common type of glial cell in the central nervous system is the astrocyte which is also called. Neuron cells bodies within the ganglia of the PNS.
And satellite cells or ganglionic gliocytes which support 2. Microglia- phagocytose foreign and degraded material in the CNS. Each Schwann cell forms a sheath around only one internode.
Microglia scavenge pathogens and dead cells. Myelination of peripheral axons and repair after injury -Oligodendrocytes. Axon cell body They consist of three parts.
Chapter 11 Describe the locations and functions of Schwann cells and satellite cells also the repair of neural damage STUDY. And Schwann cells Satellite cells and Müller cells found in the. Describe the series of events which occur at a synapse.
Remember these cells and their location with the mnemonic COPS Central - Oligodendrocytes Peripheral - Schwann. Schwann cells Neurons are specialized nervous tissue cells that function to conduct signals to and from and the brain. Damage can only be repaired if.
In addition we describe three different methods to evaluate axonal regeneration using quantitative methods. After injury Schwann cells in the PNS form a regeneration tube which is believed to secrete chemicals that attract the growing. These protocols constitute a valuable tool to analyze in vitro mechanisms associated to axonal degeneration and regeneration of sensory neurons and the role of Schwann cells in these processes.
On the other hand Schwann cells are found in the peripheral nervous system.

Organization Of Myelinating Schwann Cells Schematic Organization Of Download Scientific Diagram
What Is Myelin From A Structural Perspective Where Does The Schwann Cell Component End And The Fatty Acids Begin Quora
No comments for "Describe the Three Different Forms of Schwann Cells"
Post a Comment